Will AI Take Your Job? Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace

With the increase in popularity of Artificial Intelligence one threatening question comes to mind: Will AI Take Your Job? Especially considering the recent developments in generative AI, one might worry and wonder what to do to stay ahead of the curve. In this article, we will explore how a growing number of businesses have already implemented AI, where the journey might go, and how you can prepare to keep or even upgrade your job. One thing is for sure: Artificial Intelligence in the workplace will change the way we approach problems and bring automation to the next level.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence and the growing influence of AI in the Workplace
Before we take a close look at the impact on the job market, we need to understand what AI actually is and how AI works.
What is AI and how does it work?
First of all, Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is a really broad spectrum in computer science. The general goal is to mimic the intelligence of living beings, especially human intelligence. It can range from neural networks that try to simulate neural activity to algorithms that can handle huge amounts of data in a fraction of a second. Those algorithms can be used to make predictions and recommendations based on the input they are given. Google, YouTube, Spotify, and Netflix are just a few examples of apps and websites that use AI algorithms to make predictions and generate recommendations.
Human language processing is a sub-field of AI that is making huge advancements right now. Those AI algorithms attempt to understand and communicate in human languages.
A brief overview of the Evolution of AI
AI was conceptualized in the 1950s by Alan Turing and John McCarthy. They explored the thought-provoking idea of how close machines could get to human thinking. They experimented with algorithms that can only perform very specific tasks. As computers became more powerful from the 70s up until the 90s, those algorithms became more sophisticated and more flexible, but still bound to specific tasks and use cases. Human language was still too complex to master due to the limited computational power. As our hardware progressed and became more and more powerful, so did the algorithms and their capability. This new computational power allowed for “big data”, which analyzes huge amounts of data in a short period of time and allows to make statistical conclusions. It also opened the door for brute force problem-solving, where simply every single possibility of that problem is explored and tested to find the best possible outcome.
In recent years, human language processing algorithms evolved exponentially fast. In combination with big data and other algorithms (like image processing algorithms), we now have access to something called “generative AI”. As the name suggests, those tools can generate unique and seemingly “creative” output based on our input. We can use human language to describe what we want the AI to do. In just a few seconds (or even less than a second by now) the AI can generate text, images, audio, video, and all kinds of content.
If you are interested in more details on the history of AI, Harvard University has an excellent article on this topic: https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2017/history-artificial-intelligence/
How does AI impact the work environment?
Computer algorithms have been used in the workplace for over half a century to automate simple and repetitive tasks. With the advancements in AI, the level of automation is going to increase even further. Generative AI, especially human language processors, can now be deployed in the service sector. AI chatbots, for example, can answer common customer questions without a human touch. We all know those annoying automated phone bots of call centers that already existed for a while now. So far, most of them were pretty useless to customers because they could only answer a pre-recorded set of questions. Utilizing generative AI, those voice chatbots could be expanded to answer any type of question. They could even respond to emails with unique answers. But it doesn’t stop there, in less than a second, AI could compile company statements, analyze and summarize data and generate charts and illustrations. As you can see, those tasks would directly impact secretaries, data analysts, clerks, call centers, and administrative assistants.
The Impact of AI on Employment: A Double-Edged Sword
On the one hand, it’s easy to see how AI could replace a lot of jobs. We have seen it in the past in manufacturing where machines perform tasks fully automated more efficiently and faster than humans could. Various office jobs could face a similar fate.
On the other hand, AI could open the door to band new jobs and entire industries that no one has thought about before. Furthermore, some jobs might not be replaced but completely transformed into something new that is more efficient. Going back to the parallel in manufacturing: handmade manufacturing shifted to machined manufacturing. Instead of doing everything by hand, we now have machine operators. It’s a shift in skills. Similarly, we can expect a shift in skills in the office world. Only those who are willing to acquire the new skills will keep their jobs.
AI and Job Displacement: The Fear of Automation
Considering the level of automation in so many industries, it’s no wonder that people get scared of new technology when it reaches maturity. Here is a list of potential jobs that might be heavily influenced by the exponential growth of AI:
- Assembly Line Workers: AI-powered robots are already performing tasks previously done by humans. This trend is likely to continue and expand to other manufacturing sectors.
- Data Entry Clerks: AI and machine learning algorithms are becoming increasingly better at accurately transcribing and entering data, making manual data entry jobs highly susceptible to automation.
- Telemarketers: Since this role involves following scripts and does not require deep understanding or empathy, AI applications like chatbots and automated voice systems are likely to take over.
- Bookkeeping Clerks: Basic accounting tasks, like data recording and report generation, are being automated by AI-powered software, reducing the need for human bookkeepers.
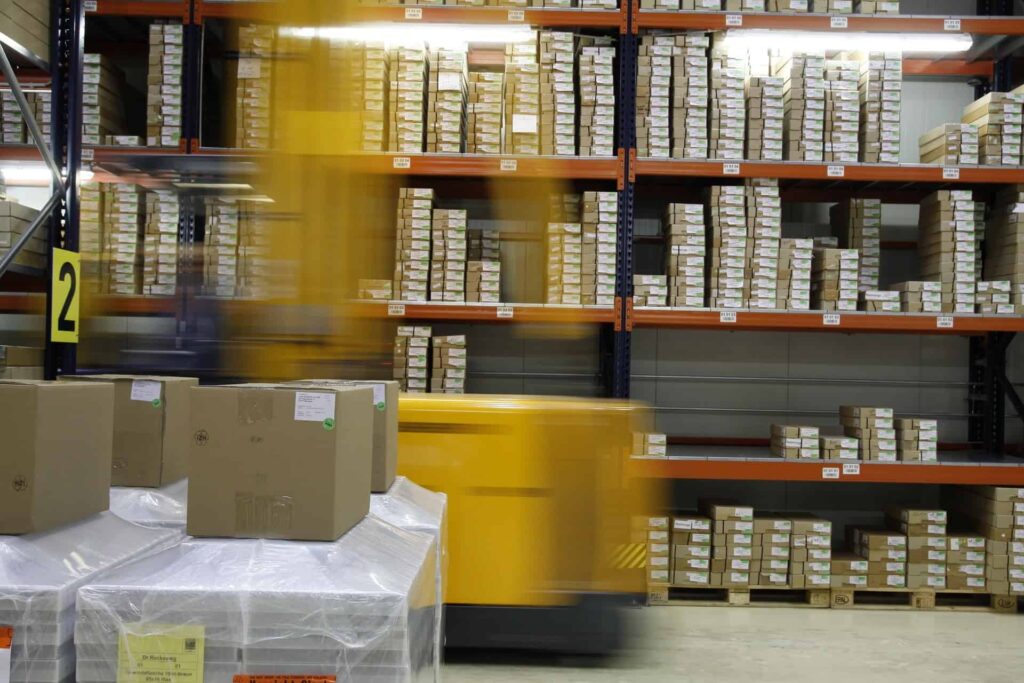
- Warehouse Workers: Automation and robotics are being widely adopted in warehousing and logistics. AI-powered robots can sort, pack, and ship goods, often more efficiently than human workers. This is already put into practice at Amazon’s warehouses.
- Cashiers: Self-checkout kiosks and AI-powered shopping systems (like Amazon Go) are automating the cashier role in retail stores.
- Fast Food Workers: Certain roles in the fast food industry, such as taking orders or even flipping burgers, could be automated with AI and robotics.
Job Creation through AI: New Opportunities for early adopters
While some jobs might be taken over by AI completely, other jobs might transform and entirely new jobs might be created. AI specialists, data scientists, and robotics engineers are just a few examples of jobs that benefit from rapid advancements. Let’s have a look at occupations that can benefit from AI:
- Doctors and Healthcare Professionals: AI can analyze medical images or patient records far more quickly than humans, highlighting anomalies and potential issues. AI doesn’t replace doctors but instead gives them valuable information to make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Teachers and Educators: AI-driven personalized learning tools can adapt to each student’s unique learning style and pace, providing customized educational content. Instead of replacing teachers, AI frees them from some administrative tasks and allows them to focus on teaching and mentoring.
- Customer Service Representatives: AI-powered chatbots can handle basic queries and issues, which can free up customer service reps to deal with more complex customer problems. The representatives’ roles transform from handling routine questions to managing more challenging and rewarding interactions.
- Data Analysts: Going through massive data sets, and identifying patterns, trends, and insights is tedious and a perfect job for AI. This can help data analysts to make more informed decisions and strategic recommendations.
- Journalists: Writing basic news reports, especially for areas like sports or financial news is easily done by generative AI. Utilizing those writing tools, journalists can focus on in-depth investigative reporting or complex storytelling.
- Lawyers: With AI we can automate tasks that can be time-consuming for lawyers, such as legal research and document review. Having AI tools at hand allows lawyers to spend more time on client consultations, court appearances, and strategy development.
As you can see, if used correctly, AI-based tools have the potential to boost efficiency to unseen levels. It’s a tool that we need to learn how to use correctly for our own benefit.
How to prepare for the potential impacts of AI on job security
Whether AI will take your job or not greatly depends on your willingness to adapt and learn new skills. AI literacy in today’s job market might be low, but it’s growing exponentially. This is why there is so much fear behind automation through AI. To remain confident, it’s a good idea to spend time learning about the new AI tools. AI Tool Insights is a great starting point for this journey. Acquiring new skills and understanding how AI technology is impacting your sector will allow you to anticipate the upcoming changes to stay ahead of the curve.
On top of knowing how to use AI tools, it’s wise to also focus on skills that are resistant to automation such as creativity, communication, empathy, and emotional intelligence.
Real-World Examples: Companies that already use AI
Nothing speaks more for a technology than companies successfully employing it in their day-to-day business. Bloomberg, for instance, is using generative AI to quickly publish financial information that is obtained by scanning through earnings statements. In retail and e-commerce, AI is nothing new anymore. AI has been used to generate personalized product recommendations and product search results. The Chinese company Alibaba wants to take this approach to the next level. AI can now be used to generate product descriptions, which makes selling to a multi-national customer base much easier and less people-intensive. One of their algorithms, for example, can predict how much demand there will be for a certain product at a given time frame in the future and automatically initiate restocking of the appropriate products even before they go low in stock. Alibaba’s AI can also handle customer inquiries and manage advertising campaigns. With their launch of the “Alibaba Cloud”, they offer AI-assisted financing solutions, AI-guided transportation solutions as well as “smart” education assistants.
Conclusion: Will AI Steal Your Job or Transform it?
In conclusion, the impact of Artificial Intelligence in the workplace is undeniable. As our technology advances, we are likely to see further integration of AI into our jobs, potentially revolutionizing the way we work. There may be fears of displacement and job loss, but it’s equally important to recognize the transformative opportunities and job creation potential that AI holds. By understanding AI technology and adapting to its rapid evolution, individuals can not only safeguard their job security but even enhance their career prospects. Therefore, while AI is here to stay, the fear of job loss should not overshadow the potential for growth, efficiency, and innovation that it brings to the table. Embracing change, acquiring new skills, and fostering uniquely human qualities such as empathy, creativity, and emotional intelligence will be key for individuals to thrive in the AI-augmented future of work.
The proactive approach would be to learn how to master this new technology as soon as possible. Be an early adapter and learn all about AI tools at our website AIToolInsights.com.










